EXPLORER-HCM
The efficacy of CAMZYOS was evaluated in EXPLORER-HCM (NCT-03470545) a Phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter, international, parallel-group trial in 251 adults with symptomatic NYHA class II and III obstructive HCM, LVEF ≥55%, and LVOT peak gradient ≥50 mmHg at rest or with provocation.
Patients on dual therapy with beta blocker and calcium channel blocker treatment or monotherapy with disopyramide or ranolazine were excluded. Patients with a known infiltrative or storage disorder causing cardiac hypertrophy that mimicked obstructive HCM, such as Fabry disease, amyloidosis, or Noonan syndrome with left ventricular hypertrophy, were also excluded.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either a starting dose of 5 mg of CAMZYOS or placebo once daily for 30 weeks. Treatment assignment was stratified by baseline NYHA functional class, baseline use of beta blockers, and type of ergometer (treadmill or exercise bicycle).
Groups were well matched with respect to age (mean 59 years), BMI (mean 30 kg/m
At baseline, approximately 73% of the randomized patients were NYHA class II and 27% were NYHA class III. The mean LVEF was 74%, and the mean Valsalva LVOT gradient was 73 mmHg. About 10% had prior septal reduction therapy, 75% were on beta blockers, 17% were on calcium channel blockers, and 14% had a history of atrial fibrillation.
All patients were initiated on CAMZYOS 5 mg (or matching placebo) once daily, and the dose was periodically adjusted to optimize patient response (decrease in LVOT gradient with Valsalva maneuver) and maintain LVEF ≥50%. The dose was also informed by plasma concentrations of CAMZYOS.
In the CAMZYOS group, at the end of treatment, 49% of patients were receiving the 5-mg dose, 33% were receiving the 10-mg dose, and 11% were receiving the 15-mg dose. Three patients temporarily interrupted their dose due to LVEF <50%, of whom two resumed treatment at the same dose and one had the dose reduced from 10 mg to 5 mg.
Primary endpoint
The primary composite functional endpoint, assessed at 30 weeks, was defined as the proportion of patients who achieved either improvement of peak oxygen consumption (pVO
A greater proportion of patients met the primary endpoint at Week 30 in the CAMZYOS group compared to the placebo group (37% vs. 17%, respectively, p=0.0005; see Table 2).
A range of demographic characteristics, baseline disease characteristics, and baseline concomitant medications were examined for their influence on outcomes. Results of the primary analysis consistently favored CAMZYOS across all subgroups analyzed (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Subgroup Analysis of the Primary Composite Functional Endpoint
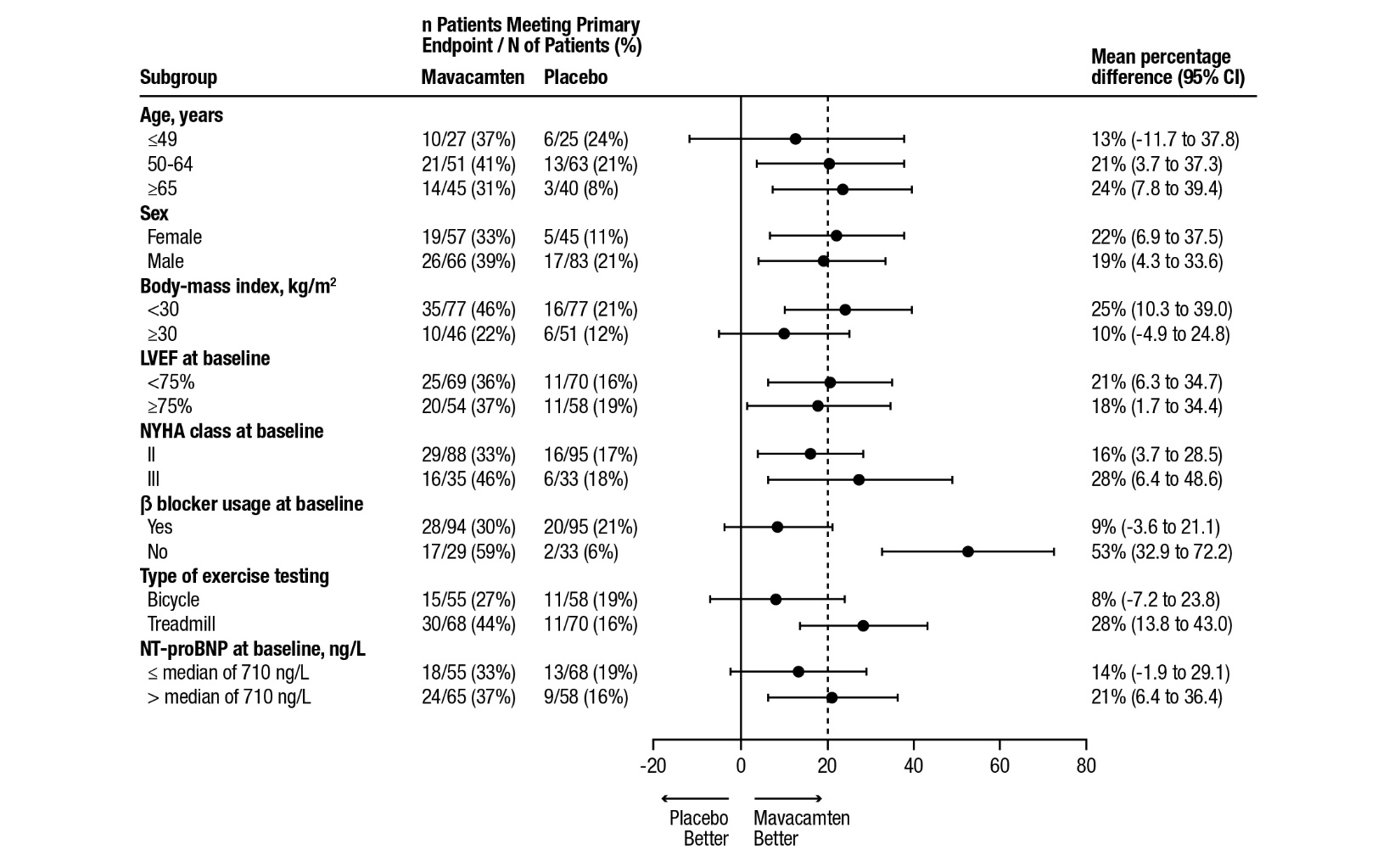
The dashed vertical line represents the overall treatment effect and the solid vertical line (no effect) indicates no difference between treatment groups.
Although the benefit of mavacamten was smaller in patients on background beta blocker therapy compared to those who were not (attenuated improvement in pVO
Secondary endpoints
The treatment effects of CAMZYOS on LVOT obstruction, functional capacity, and health status were assessed by change from baseline through Week 30 in post-exercise LVOT peak gradient, change in pVO
Figure 5: Cumulative Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 30 in LVOT Peak Gradient
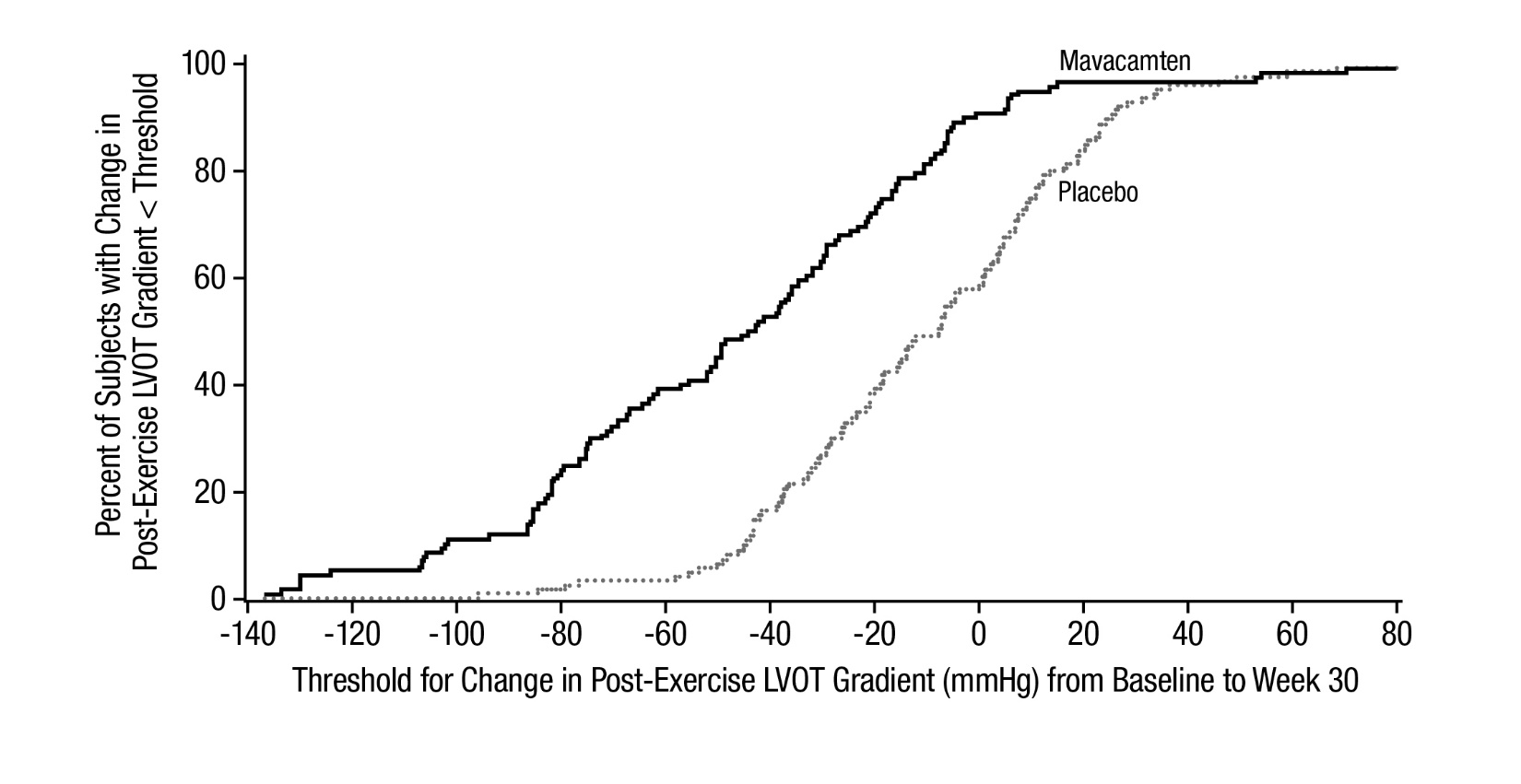
Figure 6: Cumulative Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 30 in pVO
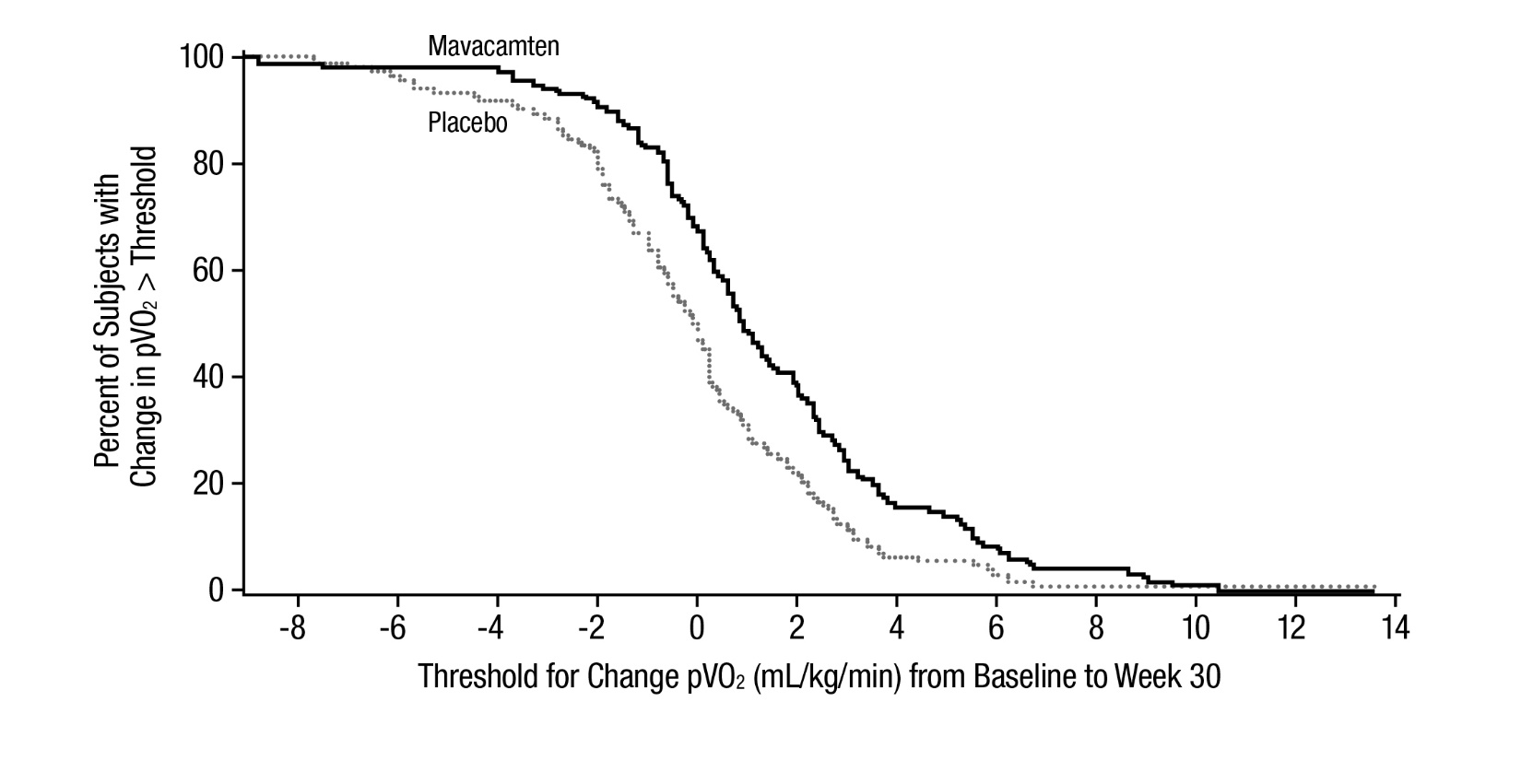
Figure 7 shows the time course for changes in KCCQ-23 CSS. Figure 8 shows the distribution of changes from baseline to Week 30 for KCCQ-23 CSS.
Figure 7: KCCQ-23 Clinical Summary Score: Mean Change from Baseline Over Time
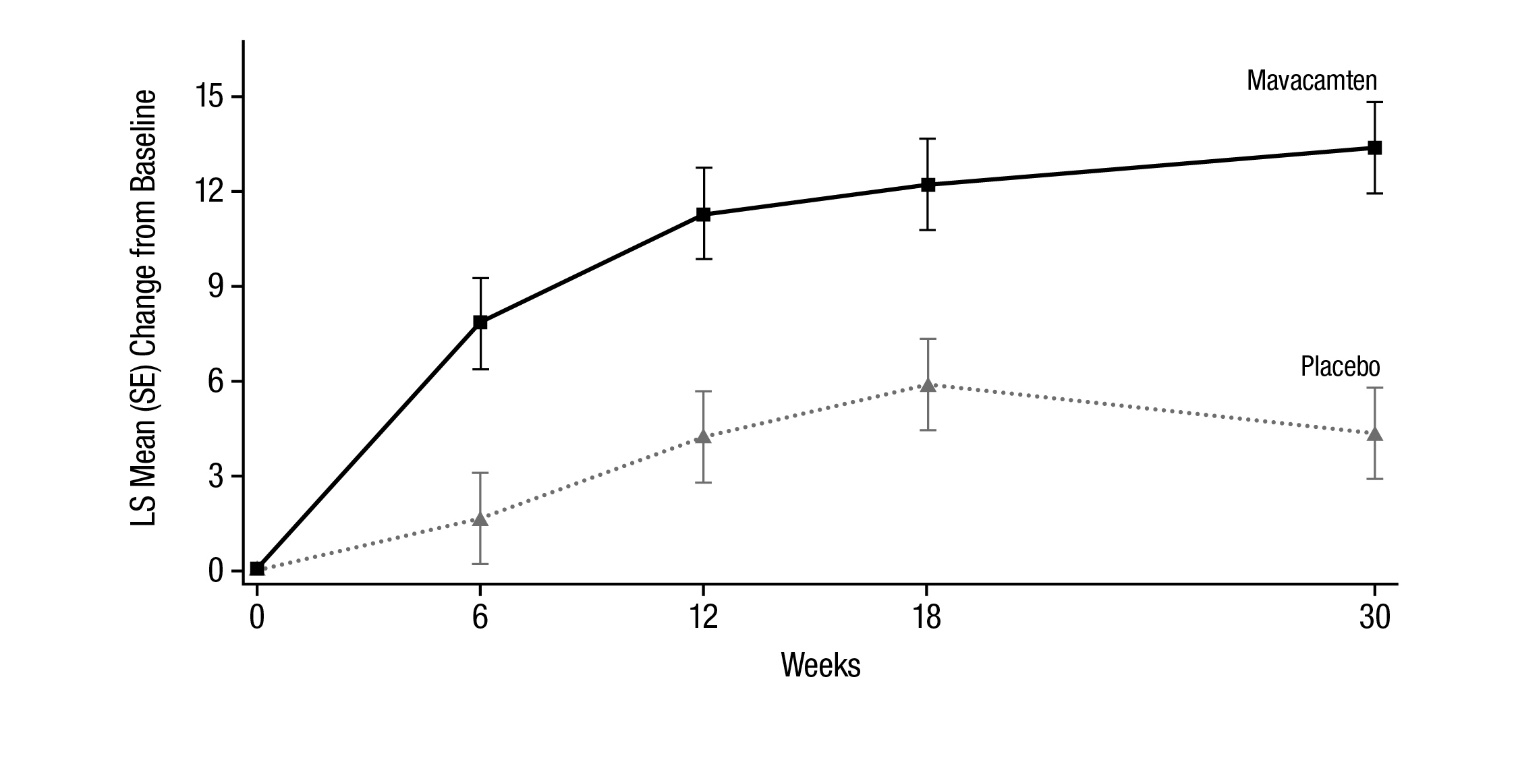
Figure 8: KCCQ-23 Clinical Summary Score: Cumulative Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 30
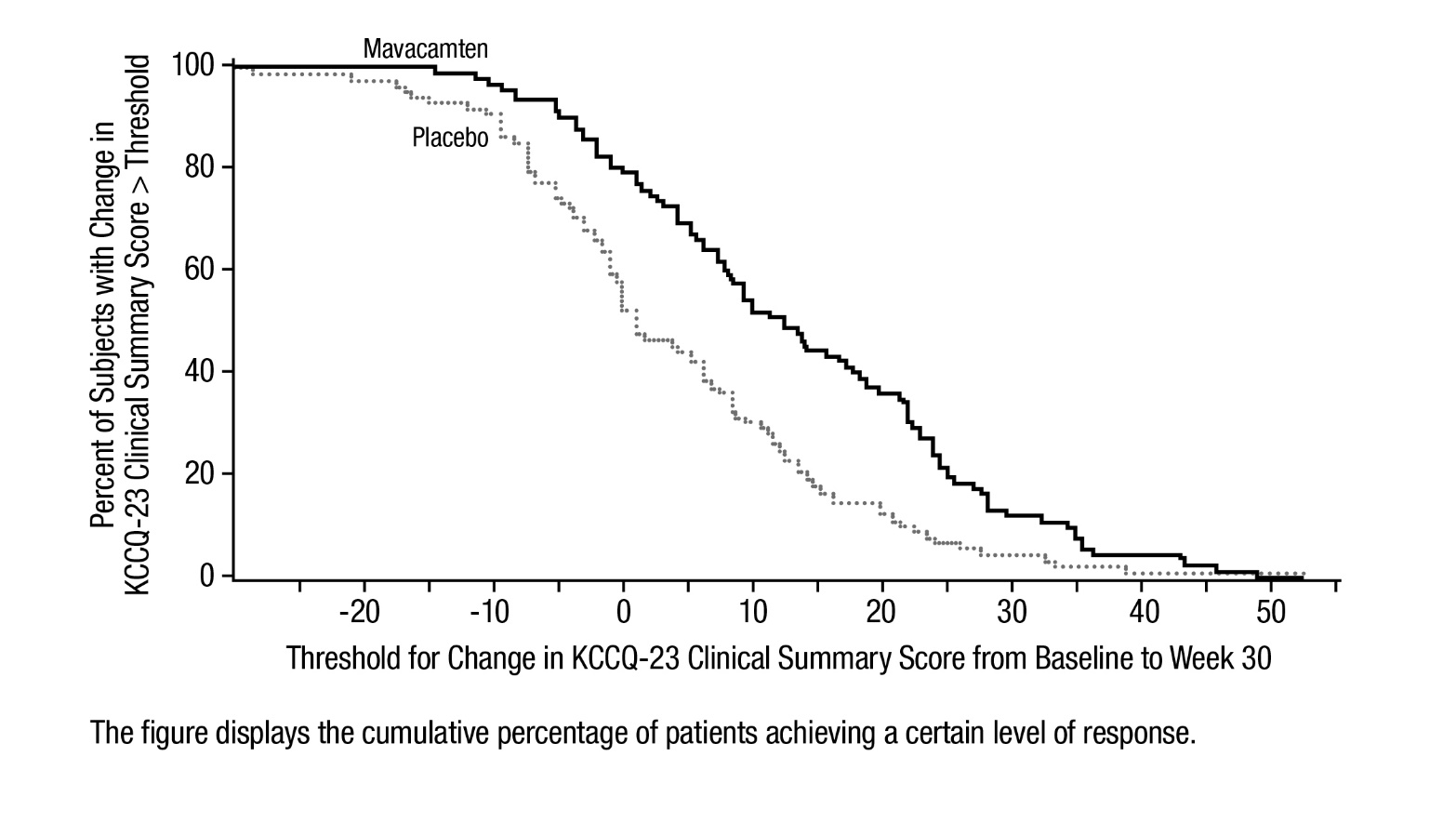
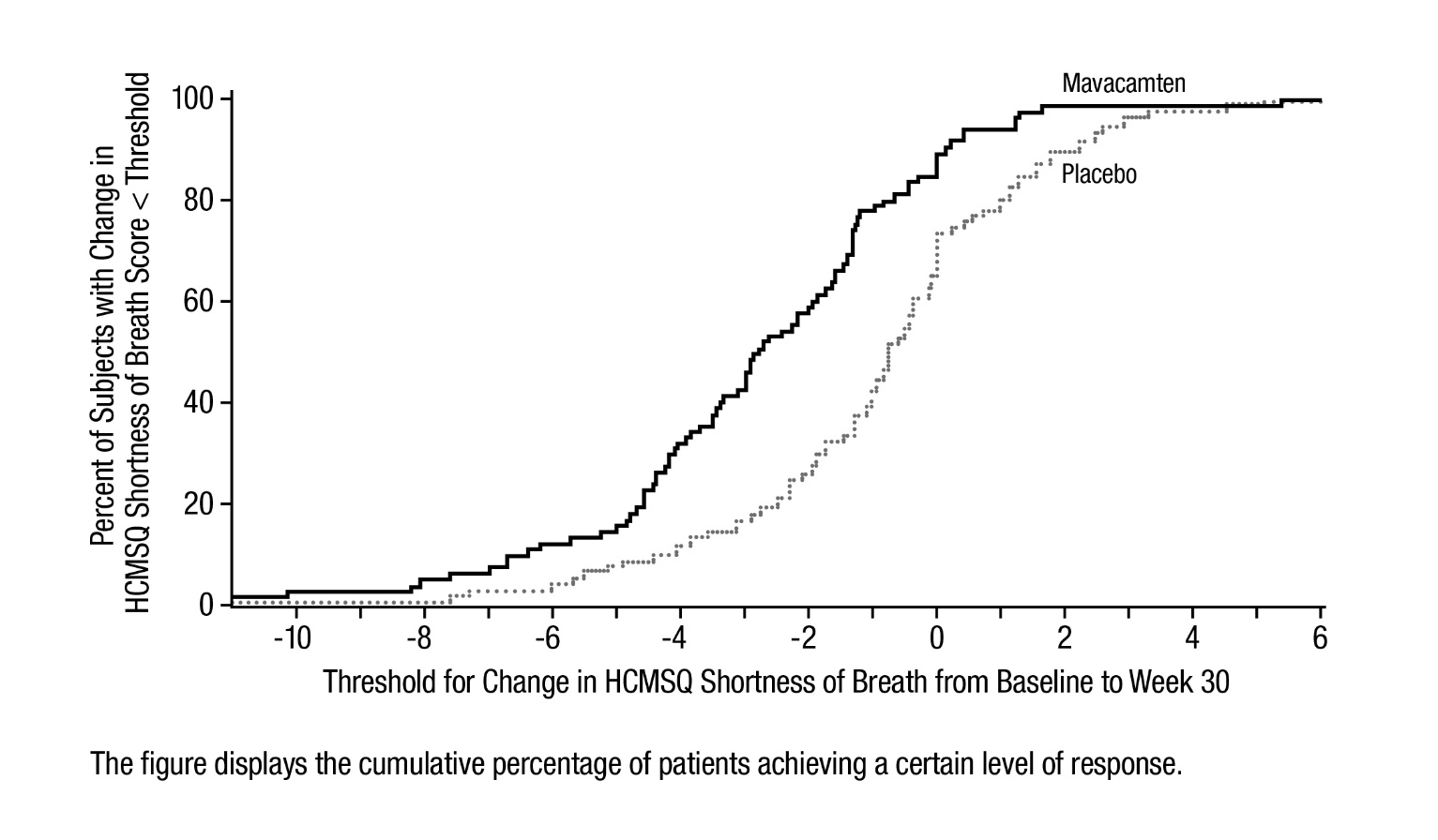
Figure 9 shows the time course for changes in HCMSQ SoB. Figure 10 shows the distribution of changes from baseline to Week 30 for HCMSQ SoB.
Figure 9: HCMSQ Shortness of Breath Domain: Mean Change from Baseline Over Time
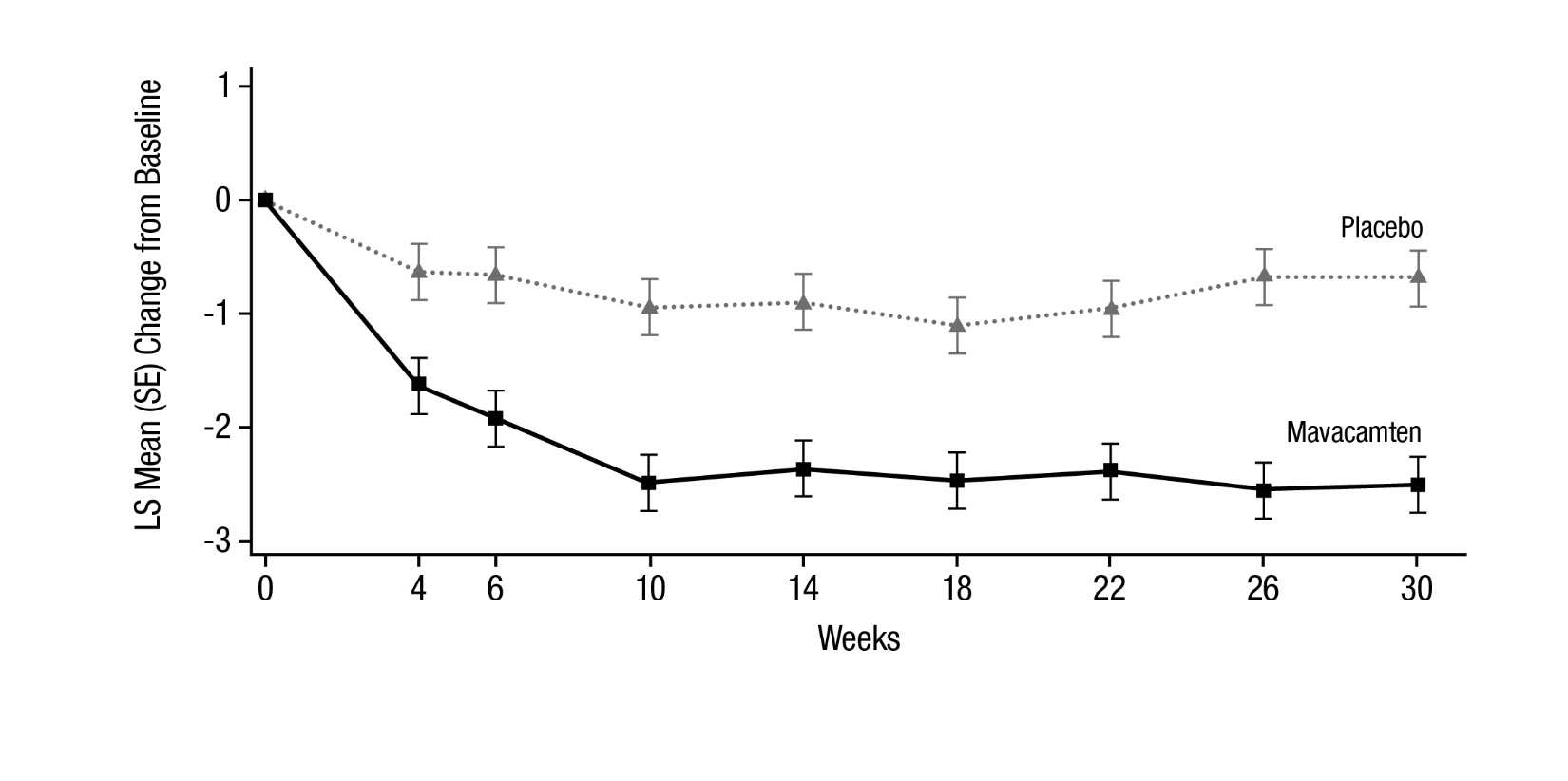
Figure 10: HCMSQ Shortness of Breath Domain: Cumulative Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 30
VALOR-HCM
The efficacy of CAMZYOS was evaluated in VALOR-HCM, a Phase 3, double-blind, randomized, 16-week, placebo-controlled trial in 112 patients (mean age of 60 years; 51% men; 93% ≥NYHA class III) randomized 1:1 to receive treatment with CAMZYOS or placebo. At baseline, all patients had symptomatic obstructive HCM and were SRT eligible.
Patients with severely symptomatic drug-refractory obstructive HCM (including 33% on any combination of beta-blocker, calcium channel blocker and/or disopyramide; 20% were on disopyramide alone or in combination with other treatment), and NYHA class III/IV or class II with exertional syncope or near syncope, were included in the study. Patients were required to have LVOT peak gradient ≥50 mmHg at rest or with provocation, and LVEF ≥60%. Patients must have been referred or under active consideration within the past 12 months for SRT and actively considering scheduling the procedure.
Patients received CAMZYOS (2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or a placebo capsule once daily for 16 weeks. Dose adjustment was based on clinical echocardiogram parameters.
Primary endpoint
CAMZYOS was shown to be superior to placebo in reducing the proportion of patients who met the primary endpoint (the composite of patient decision to proceed with SRT prior to or at Week 16 or met SRT eligibility (LVOT gradient of ≥50 mmHg and NYHA class III-IV, or class II with exertional syncope or near syncope) at Week 16 (18% vs. 77%, respectively, p<0.0001; see Table 5).
Secondary endpoints
The treatment effects of CAMZYOS on LVOT obstruction, functional capacity, and health status were assessed by change from baseline through Week 16 in post-exercise LVOT gradient, proportion of patients with improvement in NYHA class, and KCCQ-23 CSS.
Figure 11 shows the time course for changes in KCCQ-23 CSS. Figure 12 shows the distribution of changes from baseline to Week 16 for KCCQ-23 CSS.
Figure 11: KCCQ-23 Clinical Summary Score: Mean Change from Baseline Over Time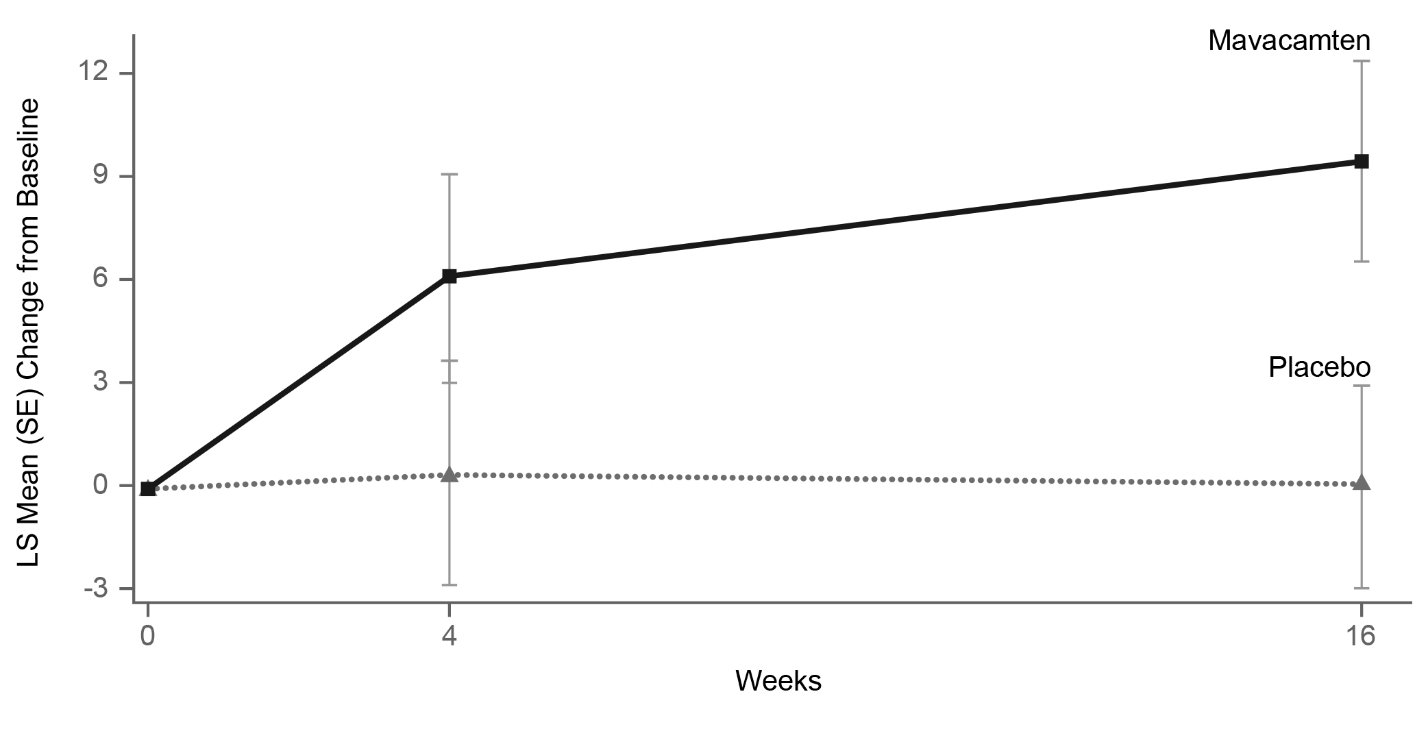
Figure 12: KCCQ-23 Clinical Summary Score: Cumulative Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 16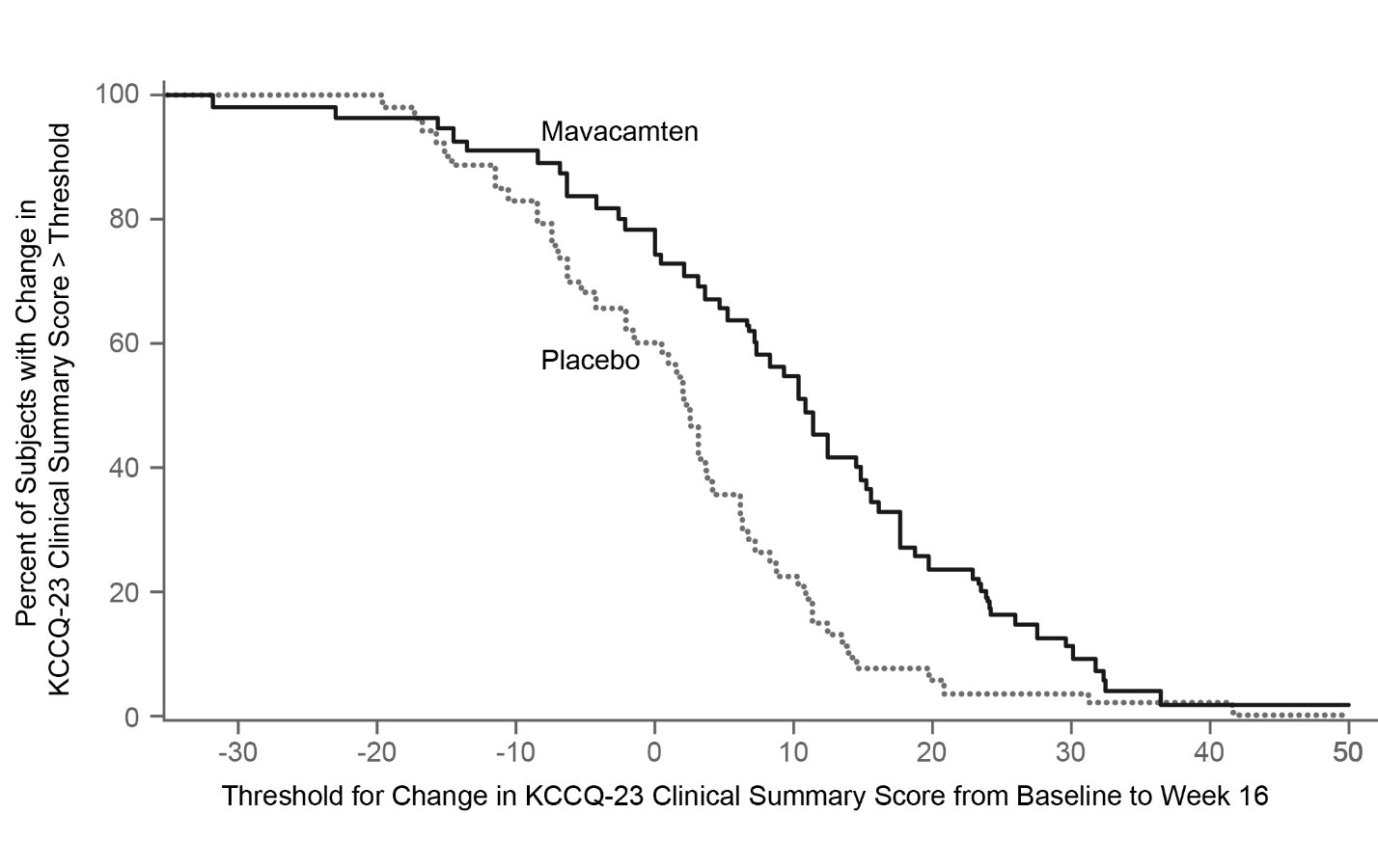 The figure displays the cumulative percentage of patients achieving a certain level of response.
The figure displays the cumulative percentage of patients achieving a certain level of response.